区间覆盖问题小结
好像接触过不少区间覆盖类的问题了,写个博客小结一下。
1,求最大覆盖次数
问题描述:相当于给你一些区间,每次给这些区间内的点值都加一(初始都为0),然后问最大的值是多少。(也就是单点的最大覆盖次数)
解决思路:显然树状数组可以很好地解决,复杂度nlogn,显得有些大材小用了。现在有一个好写复杂度还低一点的办法:把所有区间的左端点标为1,右端点标为-1,再从头到尾遍历一遍加上当前点的值,维护ans为最大值即可。
tips:为了防止一个区间的右端点和另一个的左端点重合导致答案错误,采取r++操作,可以证明不会影响结果。
代码实现:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<iomanip>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define lowbit(x) x&(-x)
typedef long long ll;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = (int)1e5 + 5;
using namespace std;
int a[maxn];
int main()
{
int n, m;//区间范围为1-n,给m个区间
cin >> n >> m;
while(m--){
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
a[l]++, a[r+1]--;
}
int t = 0, ans = -inf;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
t += a[i];
ans = max(ans, t);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}2,求最多不相交区间
问题描述:经典例题:一个人要参加一些会议,给你这些会议的开始和结束时间,问你他最多能参加多少会议。
解题思路:贪心的思想做。贪心策略:哪个越早结束就先参加哪个。结构体排序,按结束时间排,再贪心遍历求解即可。
代码实现:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<iomanip>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define lowbit(x) x&(-x)
typedef long long ll;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = (int)1e5 + 5;
using namespace std;
struct hia{
int l, r;
};
bool cmp(hia x, hia y){
return x.r < y.r;
}
hia z[maxn];
int main()
{
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
scanf("%d %d", &z[i].l, &z[i].r);
sort(z + 1, z + m + 1, cmp);
int pos = 0, sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
if(z[i].l >= pos){
pos = z[i].r;
sum++;
}
printf("%d\n", sum);
return 0;
}例题:略略略
3,求被覆盖i次的点的个数
问题描述:给你n个区间,分别求出被覆盖1-n次的点的个数
解题思路:把端点从小到大排个序,左端点标个1,右端点标个-1(实际上是右端点的后面一位,避免左端点和另一个的右端点重合情况的干扰),从左到右扫一遍,这样就能很方便地求出不同区间覆盖次数的值。
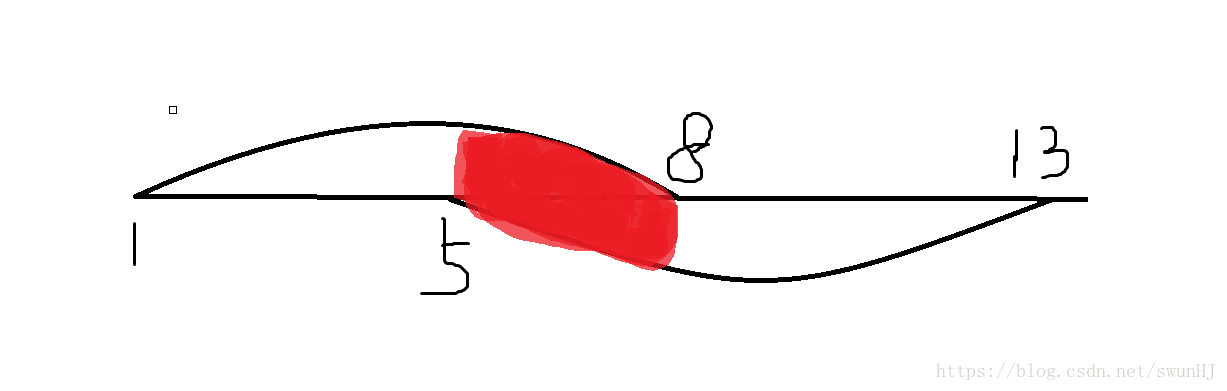
如图,给两个区间[1,7], [5, 12],用now记录当前我们加的前缀和,我们在遍历到5的时候,有cnt[1] += (5-3),(now ==1)遍历到8的时候,cnt[2] += (8 - 5),(now == 2)(其实这里是区间[5,7]的贡献,这也能解释为什么在标记的时候标记右端点的后一位),再遍历到13,cnt[1] += (13 - 8),(now == 1)。这样就能很好的完成记录。
代码:(用map显然更方便一点)
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<iomanip>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define lowbit(x) x&(-x)
typedef long long ll;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = (int)2e5 + 5;
using namespace std;
map<ll, int> m;
ll cnt[maxn];
int main()
{
int n; scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
ll a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
m[a]++;
m[b+1]--;
}
int now = 0;
ll t = 0;
map<ll, int>::iterator it;
for(it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++){
ll x = it->first;
cnt[now] += (x - t);
now += it->second;
t = x;
}
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
printf("%lld ", cnt[i]);
printf("%lld\n", cnt[n]);
return 0;
}4,求最少的能覆盖区间的区间数
大意:给一个区间[L, R],再给一些[l[i], r[i]],求用这些区间覆盖[L, R]的最少数目
解决思路:贪心解决。把这些区间以左端点进行排序,先选择第一个区间,之后的贪心策略就是选择在可选范围内的,选择右端点最大的区间。
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<iomanip>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define lowbit(x) x&(-x)
typedef long long ll;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 25005;
using namespace std;
struct hia{
int l, r;
} a[maxn];
bool cmp(hia x, hia y){
return x.l < y.l;
}
int main()
{
int n, t; scanf("%d %d", &n, &t);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
scanf("%d %d", &a[i].l, &a[i].r);
}
sort(a, a + n, cmp);
int ans = 0, i = 0, temp = 0;
while(temp < t && i < n){
ans++;
int top = temp;
if(a[i].l > temp + 1) return 0*puts("-1");
while(i < n && a[i].l <= temp + 1){
top = max(top, a[i].r);
i++;
}
temp = top;
}
if(temp < t) puts("-1");
else printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}(此代码可 AC POJ2376)http://poj.org/problem?id=2376
5,求一段区间覆盖了多少个其他的区间
大意:给你一些区间,有一些询问,每次询问给一个区间,输出这个区间覆盖了多少区间
解题思路:用二维前缀和来做。一个区间用a[l, r]来表示。询问的时候就相当于求[l, l] 到 [r, r]这个矩形中的元素数目
即sum[r][r] - sum[r][l-1] - sum[l-1][r] + sum[l-1][l-1]
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<queue>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<iomanip>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define lowbit(x) x&(-x)
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define FAST ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0)
typedef long long ll;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = (int)150000 + 5;
using namespace std;
int sum[505][505];
int main()
{
int n, m, q; scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &m, &q);
int l, r;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
scanf("%d %d", &l, &r);
sum[l][r]++;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
sum[i][j] += sum[i-1][j] + sum[i][j-1] - sum[i-1][j-1];
}
}
while(q--){
scanf("%d %d", &l, &r);
printf("%d\n", sum[r][r] - sum[r][l-1] - sum[l-1][r] + sum[l-1][l-1]);
}
return 0;
}